Maximum safety, maximum quality!
In the world of the food industry, safety is a key component of fundamental importance. We’re talking about food safety. Ensuring the safety of the produced food is not just a regulatory requirement but also a profound responsibility that spreads throughout the entire supply chain.
Lack of concern over food safety can lead to serious failures in consumer confidence, ruining the entire reputation of a company or even a determined industrial sector. In order to prevent all these potential complications, safety management takes center stage. Efficient safety management requires a comprehensive understanding of potential hazards at every step of the production process.
To assist in this task, a procedure called Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) comes into play. This strategic ally empowers industrial players to not only meet safety standards but to also elevate the entire production experience.

HACCP IN THE MANUFACTURING SECTOR
HACCP is a systematic and preventive approach meticulously created to detect, assess, and control potential hazards (biological, chemical, and physical) within industrial food processes. It minimize risks and ensures that the products reach the market with the highest quality and most importantly, that are as safe as possible.
The HACCP system is particularly focused on prevention, by identifying critical control points that serve as key monitoring points agains potential hazards. This procedure addresses seven key principals.
7 KEY PRINCIPLES OF HACCP
Although there are seven key principles of the HACCP system they are not isolated and must work in harmony with each other to create a reliable safety framework. Below we describe the seven key principles in detail.

Conduct Hazard Analysis
Identify and access potential hazards associated with each stage of the production process. The identified hazards can be biological, chemical, or even physical. This critical analysis is the foundation for a targeted and proactive approach to risk management.

Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs)
Identify specific steps where the control is crucial. These are the CCPs, where industrial operators must maintain tight control to prevent, reduce, and eliminate the previously identified hazards. An example of a CCP could be, for example, the inspection of raw materials on arrival to check for potential contaminants, ensuring that only safe ingredients are used in the production process.

Establish Critical Limits
It is important to define measurable parameters at each CCP. These critical limits set the boundaries that ensure that industrial operations stay within the safe zone, preventing the emergence of potential hazards. for example, ensuring that the internal temperature of cooked meat has reached a certain temperature in order to eliminate certain harmful bacteria.

Monitor CCPs
Define what, how, who, and how often CCPs should be monitored. Regular and proper monitoring of the established CCPs ensures that the production processes are in compliance with the established critical limits.

Establish Corrective Actions
In case any evidence is found that indicates that a particular CCP is not under control, corrective actions must be defined and implemented. This principle defines the procedures to be followed, ensuring prompt corrections and avoiding the escalation of potential risks.

Verification
The verification principle involves periodic reviews and audits. This continuous evaluation confirms that the HACCP system is a dynamic and constantly evolving process that adapts to the changing dynamics of industrial food operations, and not only a simple static set of guidelines.

Documentation
Everything related to the HACCP system, from its planning, execution, monitoring, and improvement decisions must be documented to create a comprehensive record of the system’s development, implementation, and maintenance. This documentation, in addition to ensuring compliance, also has is a valuable resource for continuous improvement.
WHY IS IT DONE?
HACCP is implemented for several crucial reasons, all of them centred around ensuring the safety of the food production process and the product that reaches consumers. Some of the primary reasons are compliance with food regulations, prevention of foodborne hazards, enhanced consumer confidence, quality control, and operational efficiency.
WHERE IS IT DONE?
HACCP systems are applied across different sectors of the food industry, from meat processing plants to restaurants and food distribution centers. Each company adopts tailored HACCP plans, ensuring they align with the specific characteristics of their operations.
KEY BENEFITS
HACCP systems in an industrial context provide considerable benefits for organizations. Overall, HACCP offers three main benefits: enhances food safety, streamlines regulatory compliance, and improves product quality. This way, HACCP not only ensures legal adherence but also enhances customer satisfaction through consistent quality control. Here are some of the key advantages of implementing a HACCP system:

Risk Mitigation
HACCP reduces the likelihood of foodborn illnesses by systematically addressing potential hazards. This proactive approach minimizes not only the consumption risks but also the likelihood of operational disruptions and recalls.

Compliance & Quality
Adherence to HACCP principles ensures compliance with food safety regulations, standards, and quality, demonstrating a commitment to consumer safety. At the same time, it also helps protect the organizations from potential legal liabilities.

Enhanced Operational Efficiency
By identifying CCPs and establishing critical limits, HACCP contributes to operational efficiency. The systematic control of key parameters ensures a streamlined production process, reducing the risk of errors.

Consumer Confidence
Consumers are more likely to trust products from companies that implement rigorous measures to ensure food safety.
MAIN CHALLENGES
In an industrial context, HACCP systems are essential, however, the correct implementation of these procedures often comes with some inherent difficulties. Here are some examples of those challenges:

Complexity of Operations
Industrial food production processes can be highly complex, involving multiple steps, equipment, and personnel. Industrial organizations may struggle with allocating the adequate personnel with the right skills to correctly develop, implement and maintain the HACCP plan.

Training and Education
Proper training and education of personnel are essential for an effective HACCP implementation. Organizations may face some challenges in ensuring that all workers are capable and aware of their responsibilities and know all specific points to successfully maintain food safety.

Cross Function Collaboration
HACCP implementation requires collaboration across different departments, and functions within an organization, including production, quality assurance, maintenance, and management. Ensuring effective communication and cooperation between all these diverse positions can be challenging.

Documentation and Record Keeping
HACCP requires meticulous documentation and record keeping to track compliance, monitor CCPs history, and have proof to demonstrate regulatory compliance. Sometimes, when it is used paper to record all this information, organizations may find it challenging to maintain accurate and up-to-date records.
HOW DIGITALIZATION CAN IMPROVE YOUR HACCP?
With the new Augmented & Connected Worker platform, it is possible to revolutionize the planning, implementation, and management of HACCP systems by digitalizing them. The HACCP digitalization will allow organizations to integrate cutting edge technology, improve worker capabilities, foster a data driven culture, and enhance a collaborative approach to ensure food safety and quality.
DIGITAL INSTRUCTIONS
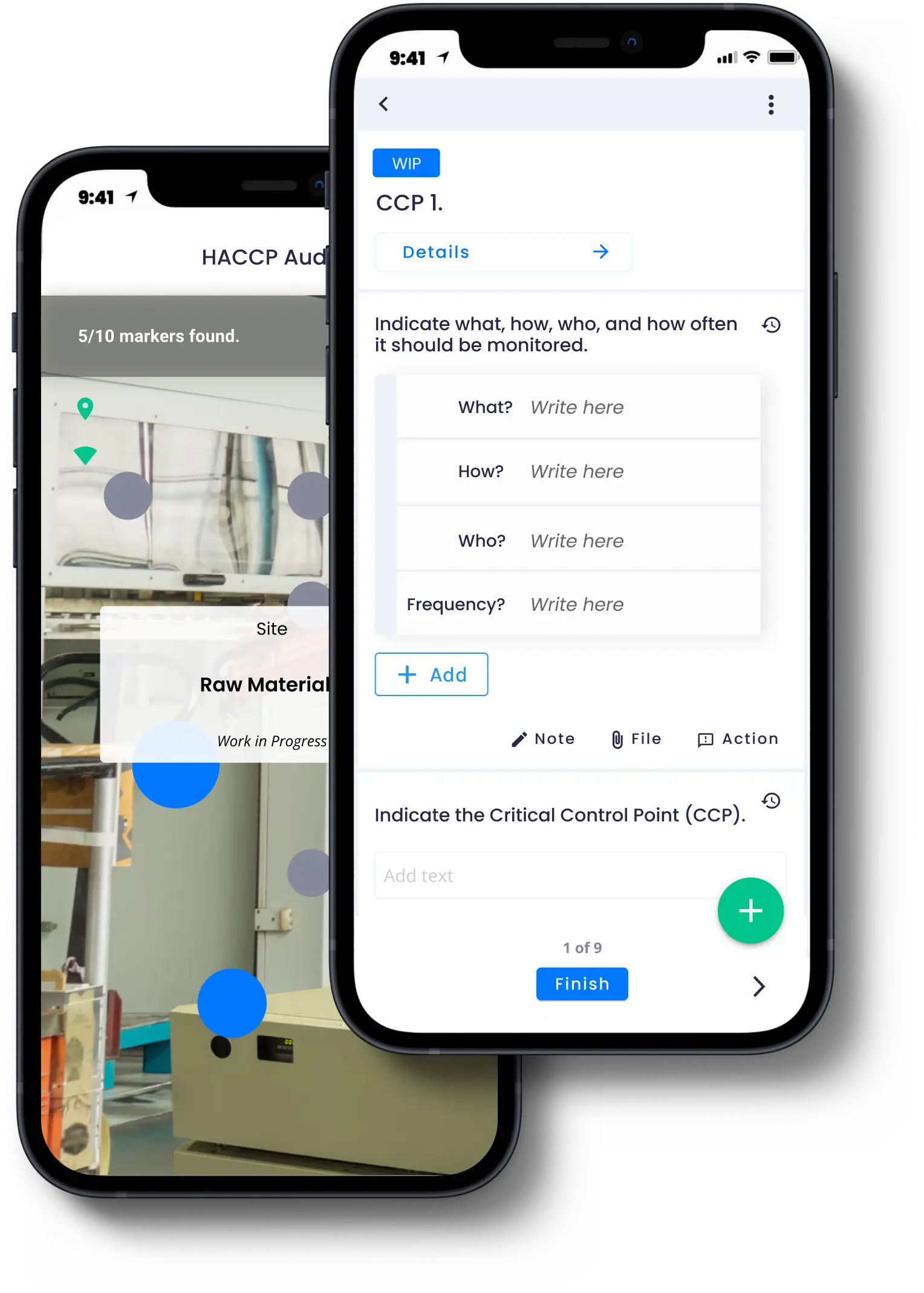
With the help of digital work instructions and checklists, the platform improves the consistency and precision of execution. It guides and facilitates the understanding of HACCP tasks that must be executed by frontline workers.
The Augmented & Connected Worker platform also offers AR guidance to overlay digital information into the physical environment, providing workers with visual guidance to execute tasks and accelerating the learning curve in training programs.
Glartek solution also acts as a central hub for information exchange. It enables real-time collaboration and communication enhancing teamwork and problem-solving by seeking clarification on procedures or sharing documents and observations.
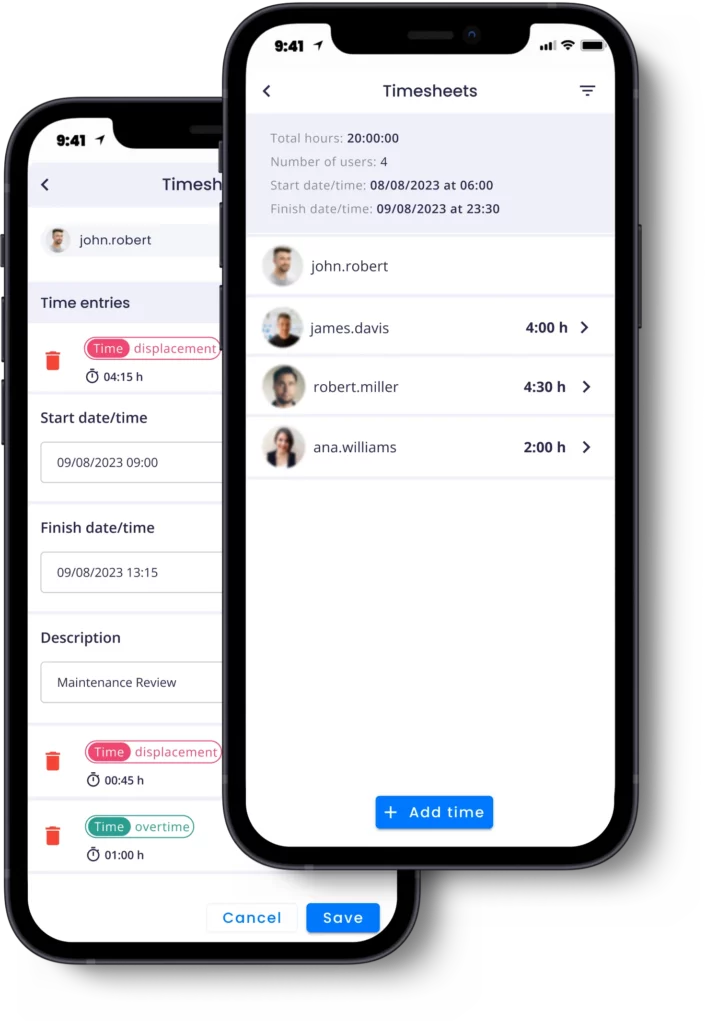
TIME & SKILLS MANAGEMENT
The Augmented & Connected Worker platform also enhances managers’ organizational capabilities by helping to plan, implement, and organize HACCP procedures and necessary resources. For example, by using timesheets managers are even capable of organizing and monitoring workers’ and teams’ activities and times.
In addition, through the platform skills matrix managers will also be able to monitor and track the required skills to execute specific procedures. This ensures that frontline workers have the necessary qualifications to execute tasks, promoting compliance and proficiency in the HACCP execution.
REAL-TIME MONITORING, ALERTS, AND DATA ANALYSIS
The platform enables real-time monitoring of CCPs, allowing personnel to track parameters and receive alerts, enabling immediate detection of deviations from critical limits and timely alerts to prevent potential hazards.
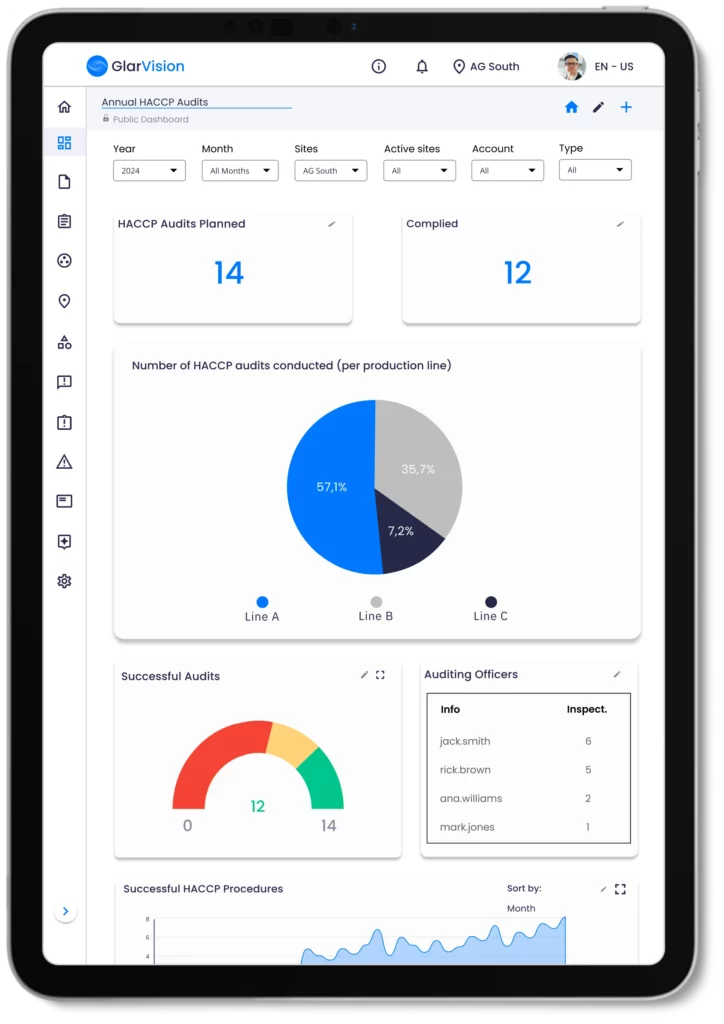
Glartek’s solution also centralizes all information and facilitates the analysis and visualisation in real-time of data collected. Advanced dashboards and reports can help identify trends, patterns, and correlations, providing valuable insights for decision-making and continuous improvement.
HOW TO MIGRATE A HACCP PROCEDURE TO THE PLATFORM?
Digitalizing a HACCP procedure is simple and can be done using the Augmented & Connected Worker platform. Using the back office you can create a digital procedure template to plan or manage the procedure.
Migrating the procedure checklist is easy due to a user-friendly form builder that allows users to replicate former paper instructions. It’s also possible to request varied types of questions with different response formats. You can also add conditional questions, scored questions, or ask for proof by requesting the upload of photos and videos, among other features.
- Create a work order template (e.g.: HACCP Plan)
- Create your tasks (e.g.: Critical Control Point #1,…)
- Create your checklist and instructions (e.g.: Identify the potential hazard?; Define the critical limits;…)
- Create a work order using the previously created template
- Assign the work order to a team or person to execute it
- Monitor the procedure and analyse the results
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, HACCP systems play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and quality of food products within industrial organizations. Transitioning from paper-based to digital HACCP system with the help of the Augmented & Connected Worker streamlines the process and improves the procedure efficiency, accuracy, and control. Ultimately, embracing the digitalization of HACCP procedures is a strategic investment that reinforces the commitment to food safety, quality, and consumer trust.
Want to learn more about HACCP and other procedures that can be migrated from paper to digital? Visit our website procedures page and discover the Augmented & Connected Worker benefits. In addition. you can also request a HACCP procedure template.
Learn More
Interested in learning more about digital solutions and how they are changing shop floors? Explore our use cases or reach out to our team to schedule a free demonstration to understand the full potential of Glartek’s Augmented & Connected Platform.



